Nail fungus, known among professionals as onychomycosis, is a very common pathology. The injury affects approximately 40% of people at least once in their lives. In this case, fungus on the feet is more common than on the hands.
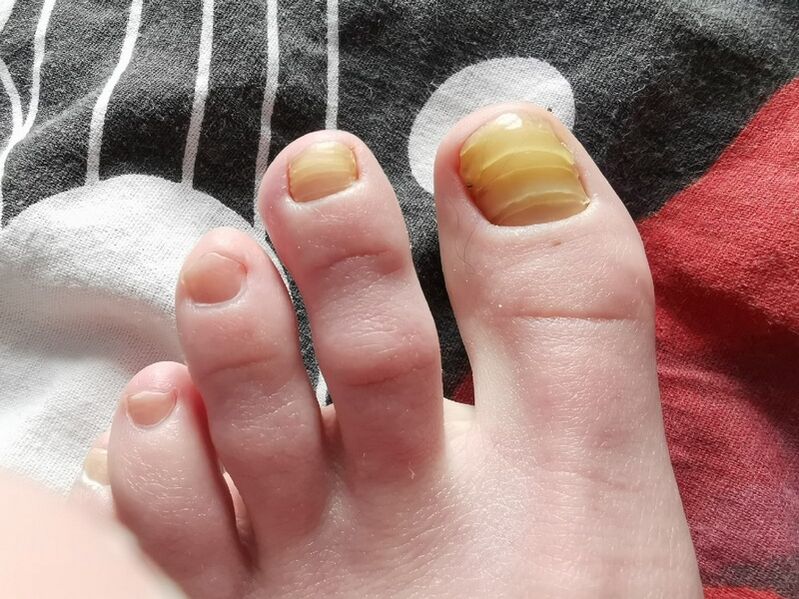
The disease begins with the appearance of a white or yellowish-brown spot under the tip of the nail. As the fungal infection penetrates deeper into the skin, the nail plate begins to discolor, thicken and crumble at the edges. If treatment is not started early, onychomycosis begins to affect the areas between the toes and can even affect the skin of the feet. The neglected fungus is called epidermophytosis. Be sure to consult your local doctor!
How can you get nail fungus?
Because the disease is infectious, you can only become infected through contact. There are hundreds of different types of pathogens in the environment. But completely healthy people with strong immunity are not susceptible to nail fungus. For the development of onychomycosis, a combination of several factors is necessary: health problems (for example, after a recent acute respiratory viral infection), as well as small cracks in the nails and surrounding skin. In addition, after the penetration of pathogenic bacteria, it is necessary to create a humid and warm environment favorable for reproduction.
Other risk factors that increase your risk of developing nail fungus include:
- microtrauma of the nail plates;
- diabetes;
- take immunosuppressants;
- congenital thickened nail plates;
- venous insufficiency (poor blood circulation in the legs);
- peripheral arterial disease;
- advanced age;
- fungal skin infections.
People who notice nail injuries frequently should take some steps to prevent recurrences. At the very least, you need to keep your feet dry and warm. You should not walk barefoot in public places, especially in swimming pools, saunas and spas. Professional athletes, people who perform intense physical work most of the day, should also pay attention to choosing the right shoes and socks. Feet should not sweat and nails should not be squeezed.
Who should I contact if I have nail fungus?
There are many effective over-the-counter medications that can be used for treatment without a prescription. But if new growths appear on the nails for the first time, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist or podiatrist. The fact is that fungi are not the only possible cause of nail problems. Many other pathologies can be similar to the manifestations of fungal infections. For example, some forms of psoriasis can mimic symptoms that occur with nail fungus. Therefore, a specialist doctor must make the diagnosis and select treatment. In the future, in case of relapse, the patient will be able to reuse medications already prescribed.
Symptoms, diagnostic methods
Before prescribing treatment for a fungus, a good doctor should refer the patient for laboratory tests. Even an experienced specialist cannot determine the type of pathogen with the naked eye. Most often, the patient is asked to send clippings of the affected nails to the laboratory for microscopic examination.
If the selected treatment methods do not help, you will need to consult a doctor again. Symptoms that indicate that nail fungus is progressing:
- micro bleeding around the nail bed;
- swelling and pain in the affected area;
- complete deformation of the nail plate;
- the appearance of a characteristic pulsation when walking;
Only after identifying the true cause of the infection is truly effective treatment possible.
Treatment options
There is no best or ideal treatment method. The medical prescription directly depends on the severity of the condition and the type of microorganism that caused the disease. Most often, doctors prescribe medications that need to be applied directly to the nail or orally. Let's take a look at each option.
Oral antifungal medications.
They are the first choice option, the most common treatment method for recurrent fungi. The tablets help the new nail grow clean and with the correct structure. You need to prepare yourself for the fact that the results are not quick: the entire treatment takes 6 to 12 weeks. Discontinuation of oral therapy is only permitted when the nail is completely clean and healthy.
As for the disadvantages, the therapy is not recommended for elderly people over 65 years of age, as well as for people who have liver problems or have been diagnosed with congestive heart failure. Additionally, oral antifungal medications can cause side effects such as rashes and nausea. It is strictly forbidden to start taking these medications without preliminary testing. In addition, approximately 2 weeks after starting treatment, it is recommended to do a scraping again to check exactly how the body reacts to the prescribed medications.
Healing varnish.
If the nails are affected for the first time (the beginning of the disease is diagnosed) or the fungus was detected in the "point phase", the doctor may prescribe the use of a special antifungal varnish with the main active ingredient. For best results, it is recommended to treat the affected nail plates and surrounding skin at least once a day. After seven days, it is necessary to remove the accumulated layers of varnish with medical alcohol, evaluate the result and repeat the course if necessary. The product quickly removes small patches of fungus, but if the lesion is deep enough, there is a high risk of relapse.
Antifungal cream.
If the lesion has spread under the nail, into the surrounding skin, it is more advisable to use a cream rather than varnish. Before each use, you must wash and dry your feet well and file the affected layer of the nail plate. Then you need to apply the cream in a thin layer. If the infection has spread to the surrounding skin, which has also become thickened, before starting treatment, it is recommended to additionally apply urea cream to soften it. Antifungal nail creams are quite effective and rarely cause complications.
If the disease occurs against the background of diabetes, then not only a podiatrist, but also an endocrinologist will be involved in developing a treatment program. Experts will ensure that prescribed medications do not conflict with each other. The fact is that even minor foot problems in diabetics can turn into full-blown gangrene.
Don't think that a fully completed treatment will automatically mean your nails will look aesthetically pleasing. Unfortunately, the destruction of the fungus does not mean that the nail plate will return to its natural color and shape. A full update can take up to 18 months.
When to resort to surgery?
If the fungus constantly reappears and stops responding to the medications used, the best option is to seek help from a surgeon. The specialist will suggest removing the affected nail completely so that the antifungal medication can be applied directly to the skin. The only, but significant, disadvantage of the method: sometimes the new plate becomes thin, already deformed. Surgical removal is also performed if the nail is so deformed and damaged that podiatric hygiene does not help to correct the situation. The operation is also indicated for patients who cannot take pills or use external agents due to individual intolerance.
Prevention methods
Following all the doctor's recommendations is the key to a successful treatment result. But sometimes the fungus returns due to weak immunity or ignorance of hygiene rules. Simple preventive measures to help avoid relapses:
- keep your feet clean and dry;
- wear flip-flops in public swimming pools, showers and changing rooms;
- carry out general cleaning and disinfection of all surfaces in your own bathroom;
- change socks every day;
- for those who wear shoes barefoot, it is recommended to wash the insoles at least once a week and, after the fungus worsens, install new ones or use insoles;
- remove tight shoes and socks that are too tight from your wardrobe;
- cut the nails short, file the edges strictly at right angles;
- wash your feet regularly, several times a day in summer;
- wear shoes that allow your feet to breathe;
After an exacerbation of the fungus, it is necessary to throw away all shoes that cannot be washed at 90 degrees or disinfected. It is also recommended to boil socks and home textiles.
Carpets should be thrown away or treated with disinfectants and antifungal detergents. Nail care tools (scissors, files, tweezers) must be sterilized after each use. During the period of exacerbation, the use of decorative varnishes, extensions or fixing artificial tips is prohibited.
Features of the course of the fungus in children, treatment methods
Nail fungus looks really ugly, but it rarely poses a serious threat to life and health. This is why adults sometimes ignore treatment. However, fungal diseases in children have their own characteristics. Changing the appearance of nails can have a profound impact on a child's self-esteem. Children may feel ugly and worry about their own health. The rapid progression of the disease can become a great stress for the baby and even cause problems with the perception of their own body and worsen self-esteem.
The parents' task is to periodically examine the child's body. After all, children often hide the growth of fungi because they believe that they themselves are to blame for the disease, they do not want to upset their elders or they are simply afraid of treatment. Parents who have discovered pathological changes in the feet should not show disapproval, disgust, or even scold the child. The phrases "you didn't wash your feet well", "it's because you rarely change your socks" are prohibited. It is necessary to talk calmly about what nail fungus is, alleviate possible fears, reassure and describe the treatment in general terms.
It is important to explain to the child that he is not to blame for the illness. But at the same time, it is necessary to convey that fungal infections love dark and damp spaces, so it is necessary to regularly change socks, keep shoes clean and not forget about daily hygiene procedures.
Fungus treatment in children is usually done with oral medications. The fact is that children's nails are very thin and grow very quickly, which means that the risk of complications after using creams and gels is greater.
Fungal infections are very common. But with high-quality daily hygiene procedures and strong immunity, the risk of infection is minimized.























